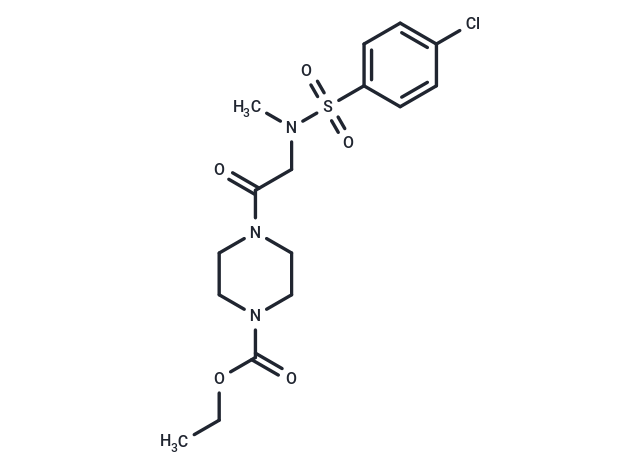
Fluorogen binding modulator-1
CAS No. 510716-65-1
Fluorogen binding modulator-1( —— )
Catalog No. M35316 CAS No. 510716-65-1
Fluorogen binding modulator-1 (Fluorogen binding modulator-1) is a nonfluorescent inhibitors of Fluorogen–Fluorogen Activating Protein Binding Pairn.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 47 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 56 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 83 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 131 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 192 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 279 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 403 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameFluorogen binding modulator-1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionFluorogen binding modulator-1 (Fluorogen binding modulator-1) is a nonfluorescent inhibitors of Fluorogen–Fluorogen Activating Protein Binding Pairn.
-
DescriptionFluorogen binding modulator-1 (PubChem SID 125240934) is a fluorogen activating protein (FAP)-fluorogen binding modulator with -log EC50s of 6.61 and 6.37 for AM2.2-β2AR and AM2.2-GPR32, respectively.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number510716-65-1
-
Formula Weight403.88
-
Molecular FormulaC16H22ClN3O5S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESS(N(CC(=O)N1CCN(C(OCC)=O)CC1)C)(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(Cl)C=C2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Wu Y, et al. Discovery of Small-Molecule Nonfluorescent Inhibitors of Fluorogen-Fluorogen Activating Protein Binding Pair. J Biomol Screen. 2016 Jan;21(1):74-87.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
D-Pantothenic acid
D-Pantothenic acid, also called vitamin B5, is a water-soluble vitamin and an essential nutrient for many animals.
-
8beta,9alpha-Dihydro...
8β,9α-Dihydroxylindan-4(5),7(11)-dien-8alpha,12-olide (compound 3), a sesquiterpene, has anti-LIMK1 activity. 8β,9α-Dihydroxylindan-4(5),7(11)-dien-8alpha,12-olide has inhibitory property on cell motility.
-
1-(3-chloropyridin-2...
1-(3-chloropyridin-2-yl)piperazine dihydrochloride is a chemical compound.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


